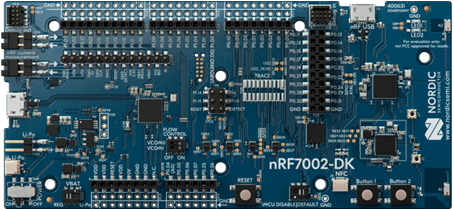
- Download the
nrf7002dk_merged.hexfile from the firmware directory. - Install nRF Connect for Desktop
- Use the Programmer application to program the Hex file onto your development kit.
NOTE: For programming, use the USB port on the left side of the picture above, which is connected to the on-board debugger/programmer.
Once programmed, you will use the USB port on the top right of the image above, which is connected to the nRF5340 chip on the board. This is where you will find the MicroPython REPL prompt.
The first time that you use the device you might need to create the filesystem. You can do that from the REPL prompt:
import os
from zephyr import FlashArea
block_dev = FlashArea(FlashArea.STORAGE, 4096)
os.VfsLfs2.mkfs(block_dev)
os.mount(block_dev, '/flash')
There are two buttons:
- Button 1: If pressed at boot time, the board will boot into the Bootloader (mcuboot) for firmware upgrades. During normal operation it can be used with
Pin.cpu.gpio1_8 - Button 2: If pressed at boot time, the board will skip executing a
main.pyfile from the filesystem. During normal operation, it can be used withPin.cpu.gpio1_9
There are two LEDs:
- LED1: Can be accessed with
Pin.cpu.gpio1_6 - LED2: Can be accessed with
Pin.cpu.gpio1_7
from machine import Pin
pin = Pin(Pin.cpu.gpio1_6, Pin.OUT)
For the nRF7002DK board, these are the available pins:
>>> Pin.cpu.gpio
gpio0_0 gpio0_1 gpio0_10 gpio0_11
gpio0_12 gpio0_13 gpio0_14 gpio0_15
gpio0_16 gpio0_17 gpio0_18 gpio0_19
gpio0_2 gpio0_20 gpio0_21 gpio0_22
gpio0_23 gpio0_24 gpio0_25 gpio0_26
gpio0_27 gpio0_28 gpio0_29 gpio0_3
gpio0_30 gpio0_31 gpio0_4 gpio0_5
gpio0_6 gpio0_7 gpio0_8 gpio0_9
gpio1_0 gpio1_1 gpio1_10 gpio1_11
gpio1_12 gpio1_13 gpio1_14 gpio1_15
gpio1_2 gpio1_3 gpio1_4 gpio1_5
gpio1_6 gpio1_7 gpio1_8 gpio1_9
>>> Pin.board.
A0 A1 A2 A3
A4 A5 D0 D1
D10 D11 D12 D13
D14 D15 D2 D3
D4 D5 D6 D7
D8 D9
The available bus is i2c1 and this is how you get an instance:
from machine import I2C
i2c = I2C('i2c1')
Most of the Python APIs for Wi-Fi access are the same as the existing MicroPython Wi-Fi APIs. Here is the documentation for the WLAN class
The auth parameter is required. You can use the the integers from network.AUTH_*, or use the value returned in the scan. For example:
nic.connect('ssid', 'passphrase', network.AUTH_WPA2_PSK)
The security field values are different for the Zephyr port:
- network.AUTH_OPEN
- network.AUTH_WPA2_PSK
- network.AUTH_WPA2_PSK_SHA256
- network.AUTH_WPA3_SAE
Return the current status of the wireless connection.
When called with no argument the return value describes the network link status.
The possible statuses are defined as constants:
STAT_IDLE-- no connection and no activity,STAT_CONNECTING-- connecting in progress,STAT_GOT_IP-- connection successful.
When called with one argument param should be a string naming the status parameter to retrieve. All the parameters refer to the access point that the device is currently connected to.
'rssi': RSSI of the current connection'ssid': SSID of the current connection'band': The frequency band being used, e.g. network.WIFI_BAND_2_4_GHZ'link_mode': The Wi-Fi generation. For example, 6 for Wi-Fi 6 (802.11ax)'channel': The channel being used'mfp': The current Management Frame Protection option. 0 - disabled; 1 - optional; 2 - required'security': The security being used.'bssid': Hardware address of the access point, in binary form, returned as bytes object.'dtim': The DTIM period of the access point.'beacon_interval': The beacon interval of the access point, in ms.'twt_capable': Whether the access point supports TWT for power savings.
Get or set general network interface parameters. These methods allow to work
with additional parameters beyond standard IP configuration (as dealt with by
WLAN.ifconfig()). These include network-specific and hardware-specific
parameters. For setting parameters, keyword argument syntax should be used,
multiple parameters can be set at once. For querying, parameters name should
be quoted as a string, and only one parameter can be queries at a time:
Following are commonly supported parameters:
'pm': WiFi Power Management setting (see below for allowed values)'wmm': 0 for Legacy power save mode, 1 for Wireless Multimedia (WMM)'wakeup': 0 for wakeup on every DTIM beacon, 1 to set a listen interval and skip beacons'listen_interval': Number of beacons to skip. For example, setting this to 10 will sleep for approximately 1 minute.'timeout_ms': The power save inactivity timer (in ms)
NOTE:
wmmandlisten_intervalparameters can only be changed when the device is not connected to an access point.
Set Target Wake Time. If the Access Point supports it, this allows the Station and
Access Point to negotiate how long to remain asleep (interval), and for how long
to be awake (wake_time). The callback is not yet implemented.
To stop using TWT and go back to the power savings settings in config, use the
teardown command.